OAROID
We securepeople
ID SCANNING.
Authenticate
Scans photo ID for validation and data extraction.
Authenticate
Scans photo ID for validation and data extraction.
FACE ANALYSIS.
Own Device
User records a live image of their face for identity verification.
Own Device
User records a live image of their face for identity verification.
OARO IDENTITY®.
Match
Analyzes face image and ID to verify authenticity of document and a positive match.
Match
Analyzes face image and ID to verify authenticity of document and a positive match.
USER VALIDATION.
Validate
Biometric record securely stored and certified using the OARO IDENTITY® blockchain.
Validate
Biometric record securely stored and certified using the OARO IDENTITY® blockchain.
PROFILE CREATED.
Digital ID
Now the user has a digital identity that can be used for credential verification, accessing specific locations, signing or certifying information.
Digital ID
Now the user has a digital identity that can be used for credential verification, accessing specific locations, signing or certifying information.
DATA SHARING.
Authorize
The user has authorize each time their data is shared or required for any use.
Authorize
The user has authorize each time their data is shared or required for any use.
Digital ID. A world of possibilities
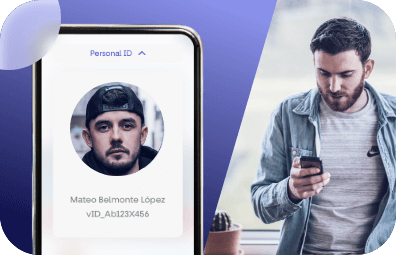
Confirm the identity of users through their phone, eliminating the need for document scans or selfies.

Facilitate swift, effortless, and secure authentication to simplify the login and transaction processes.

7,000+ identity documents can be authenticated from over 200 countries.

Achieve an 80% rate of frictionless actions, eliminating the need for human service agents in most cases.

OAROTICKETING
Ticketing Simplified

OAROTICKETING
We empower Brands
MARKETPLACE.
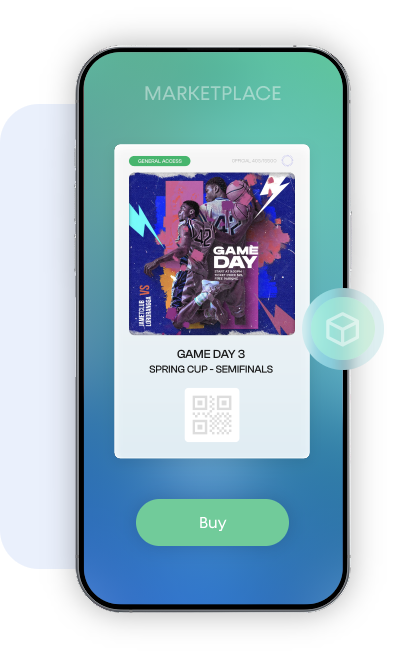
Purchase
The ticket is securely generated on the Blockchain upon completion of the purchase.
Purchase
The ticket is securely generated on the Blockchain upon completion of the purchase.
WEBSITE OR MOBILE APP.
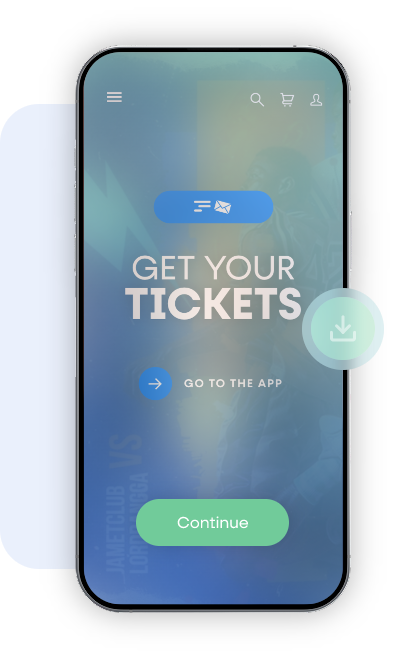
Holder
The user receives a link to the mobile ticketing app via email or SMS.
Holder
The user receives a link to the mobile ticketing app via email or SMS.
MARKETPLACE.
Resale
Once you have the ticket, the user can either retain it or list it for sale at a fixed price or in an auction format.
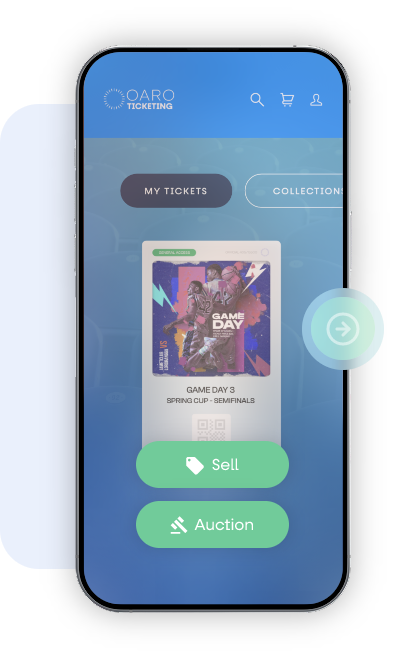
Resale
Once you have the ticket, the user can either retain it or list it for sale at a fixed price or in an auction format.
BIOMETRIC VERIFICATION.
Identification
On the designated date and time, a unique QR code, barcode, or Face ID Pattern is generated and scanned for entry. This code cannot be replicated.

Identification
On the designated date and time, a unique QR code, barcode, or Face ID Pattern is generated and scanned for entry. This code cannot be replicated.
USER AUTHENTICATION.
Access
The code is utilized for entry, with the option for facial recognition. Subsequently, the ticket is marked as used.

Access
The code is utilized for entry, with the option for facial recognition. Subsequently, the ticket is marked as used.

OARO API
OARO offers a comprehensive suite of blockchain solutions designed to revolutionize various industries by enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency in digital interactions. Our cutting-edge blockchain API forms the foundation of our offerings, enabling secure and tamper-proof data management.